-
 UN climate chief urges G20 to spur tense COP29 negotiations
UN climate chief urges G20 to spur tense COP29 negotiations
-
Philippines warns of 'potentially catastrophic' Super Typhoon Man-yi

-
 Tens of thousands flee as Super Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
Tens of thousands flee as Super Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
-
Gabon votes on new constitution hailed by junta as 'turning point'

-
 Tens of thousands flee as Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
Tens of thousands flee as Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines
-
Is Argentina's Milei on brink of leaving Paris climate accord?

-
 Fitch upgrades Argentina debt rating amid economic pain
Fitch upgrades Argentina debt rating amid economic pain
-
Trump picks Doug Burgum as energy czar in new administration

-
 At summit under Trump shadow, Xi and Biden signal turbulence ahead
At summit under Trump shadow, Xi and Biden signal turbulence ahead
-
Xi warns against 'protectionism' at APEC summit under Trump cloud

-
 Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud
Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud
-
Leftist voices seek to be heard at Rio's G20 summit

-
 Boeing strike will hurt Ethiopian Airlines growth: CEO
Boeing strike will hurt Ethiopian Airlines growth: CEO
-
US retail sales lose steam in October after hurricanes

-
 Spate of child poisoning deaths sparks S.Africa xenophobia
Spate of child poisoning deaths sparks S.Africa xenophobia
-
Comedian Conan O'Brien to host Oscars

-
 Gore says 'absurd' to hold UN climate talks in petrostates
Gore says 'absurd' to hold UN climate talks in petrostates
-
Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts

-
 China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks
-
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence

-
 Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
-
'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth

-
 Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
-
Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys

-
 Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
-
TikTok makes AI driven ad tool available globally

-
 Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
-
China retail sales pick up speed, beat forecasts in October

-
 Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
-
Mexico City youth grapple with growing housing crisis

-
 Cracks deepen in Canada's pro-immigration 'consensus'
Cracks deepen in Canada's pro-immigration 'consensus'
-
Japan's Princess Mikasa, great aunt to emperor, dies aged 101

-
 Venezuela opposition activist dies in custody
Venezuela opposition activist dies in custody
-
Policymakers defend Fed independence amid concerns about Trump era

-
 Lebanon economic losses top $5 billion in year of clashes: World Bank
Lebanon economic losses top $5 billion in year of clashes: World Bank
-
Fed Chair calls US the best-performing major economy in the world

-
 Brother of late Harrods owner also accused of sexual violence: BBC
Brother of late Harrods owner also accused of sexual violence: BBC
-
New York to revive driver congestion charge plan, drawing Trump ire

-
 China's Xi arrives in Peru for APEC summit, Biden meeting
China's Xi arrives in Peru for APEC summit, Biden meeting
-
Spain's Vanguardia daily to stop posting on 'disinformation network' X

-
 New York to revive driver congestion charge plan
New York to revive driver congestion charge plan
-
US stocks wobble as traders weigh future Fed cuts

-
 BHP, Vale cleared by Brazil court over 2015 dam disaster
BHP, Vale cleared by Brazil court over 2015 dam disaster
-
Legal migration to OECD reaches new record in 2023

-
 Central bank independence 'fundamental' for good policy: Fed official
Central bank independence 'fundamental' for good policy: Fed official
-
EU fines Meta $840 million for 'abusive' Facebook ad practices

-
 Iran tells UN nuclear chief willing to resolve 'ambiguities'
Iran tells UN nuclear chief willing to resolve 'ambiguities'
-
Coach owner Tapestry calls off Capri bid on regulatory blocks

-
 EU fines Meta 798 mn euros for Facebook ad antitrust breach
EU fines Meta 798 mn euros for Facebook ad antitrust breach
-
'Terrible' AI has given tech an existential headache: activist


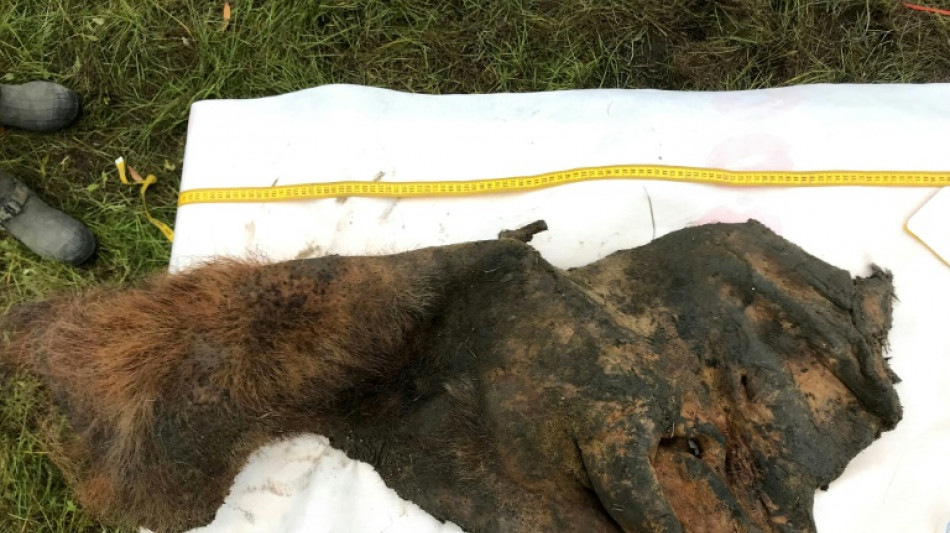
3D genome extracted from 'freeze-dried' woolly mammoth
About 52,000 years ago, the skinned hide of a Siberian woolly mammoth was exposed to conditions so frigid that it spontaneously freeze-dried, locking its DNA fragments into place.
In a study published Thursday in the journal Cell, scientists reported using this remarkable sample to reconstruct the animal's genome in three dimensions -- a breakthrough that could yield important new insights about extinct species and even boost efforts to bring them back to life.
Until now, ancient DNA specimens have only been found in short, scrambled fragments, severely limiting the amount of information researchers could extract.
"Now we show that, at least under some circumstances, it's not just those snippets of that DNA that survive, but they survive in such a way that preserves the original arrangement," co-author Olga Dudchenko, a geneticist at Baylor College of Medicine, told AFP.
Understanding the 3D architecture of an organism's genome —- the complete set of its DNA -- is crucial for identifying which genes are active in specific tissues, revealing why brain cells think, heart cells beat, and immune cells fight disease.
It was long assumed that due to the rapid degradation of very small particles, such information would inevitably be lost to history.
But around a decade ago, an international team of scientists set out to find an ancient sample where the 3D organization of the DNA remained intact such that it could be fully reconstructed with a new analytical technique.
Their quest led them to an exceptionally well-preserved woolly mammoth sample, excavated in northeastern Siberia in 2018.
Whether the hirsute pachyderm -— a female with a distinctive mullet-style hairdo -- died naturally or was killed by humans is unknown. However, it does appear that early humans skinned her, leaving tissue around the head, neck, and left ear intact, according to Dudchenko.
- Woolly mammoth jerky -
The team hypothesizes that the skin cooled and dehydrated, transitioning into a glasslike state that trapped its molecules in place and preserved the shape of its chromosomes, or the threadlike structures that hold DNA strands.
Essentially, they had discovered a piece of freeze-dried woolly mammoth jerky.
To test the resilience of jerky, they subjected lab-made and store-bought beef jerky pieces to a series of tests simulating the kind of damage ancient samples might encounter over millennia.
"We fired a shotgun at it. We ran over it with a car. We had a former starting pitcher for the Houston Astros throw a fastball at it," said Cynthia Perez Estrada, co-author of the study and a researcher at Baylor College of Medicine and Rice University.
The jerky would break into tiny bits, shattering as dramatically as window glass at times. "But at the nano-scale, the chromosomes were intact, unchanged," said Perez Estrada in a statement.
One significant discovery from their research established that mammoths had 28 pairs of chromosomes. The finding aligns with the 28 chromosomal pairs found in elephants, the closest living relatives of mammoths, "but before this study, it was anybody's guess," said Dudchenko.
- 'Fossil chromosomes' -
The team's analysis also identified several "candidate" genes which might be responsible for what made woolly mammoths woolly -- including a gene responsible for long, thick eyelashes, and another associated with sparse sweat glands.
Erez Lieberman Aiden of Baylor College of Medicine, who co-led the team, told AFP that while the researchers' goal was not to bring mammoths back, the information they gleaned could be used for such efforts.
A Japanese team is looking at cloning woolly mammoths, while a group in the United States is aiming to create genetically "mammothized" elephants.
Within the skin, "96 percent of genes are basically in the same activity state as an elephant," said Aiden, meaning that scientists working on de-extinction could now focus on the remaining four percent.
The team now hopes that the benefit of their study will extend far beyond their special sample and open a new chapter in paleogenetics if other such "fossil chromosomes" can be found.
The Arctic permafrost remains a promising place to look, and it is also possible that mummification from ancient civilizations in warmer climates could preserve genomic structures too, according to Dudchenko.
A.Zimmermann--CPN