
-
 Between laughs and 'disaster', Trump divides Davos
Between laughs and 'disaster', Trump divides Davos
-
Hundreds of people protest ahead of Swiss Davos meeting

-
 US falling behind on wind power, think tank warns
US falling behind on wind power, think tank warns
-
US news giant CNN eyes 200 job cuts, streaming overhaul

-
 Rubio chooses Central America for first trip amid Panama Canal pressure
Rubio chooses Central America for first trip amid Panama Canal pressure
-
Wall Street's AI-fuelled rally falters, oil slumps

-
 Trump tells Davos elites: produce in US or pay tariffs
Trump tells Davos elites: produce in US or pay tariffs
-
Progressive politics and nepo 'babies': five Oscar takeaways

-
 American Airlines shares fall on lackluster 2025 profit outlook
American Airlines shares fall on lackluster 2025 profit outlook
-
France to introduce new sex education guidelines in schools

-
 Wall Street's AI-fuelled rally falters
Wall Street's AI-fuelled rally falters
-
Drinking water in many French cities contaminated: study

-
 After Musk gesture, activists project 'Heil' on Tesla plant
After Musk gesture, activists project 'Heil' on Tesla plant
-
ICC prosecutor seeks arrest of Taliban leaders over persecution of women

-
 Syria's economy reborn after being freed from Assad
Syria's economy reborn after being freed from Assad
-
Shoppers unaware as Roman tower lurks under French supermarket

-
 Stocks mainly rise after Wall Street's AI-fuelled rally
Stocks mainly rise after Wall Street's AI-fuelled rally
-
Singer Chris Brown sues Warner Bros for $500 mn over documentary

-
 J-pop star Nakai to retire after sexual misconduct allegations
J-pop star Nakai to retire after sexual misconduct allegations
-
Leaky, crowded and hot: Louvre boss slams her own museum

-
 WWF blasts Sweden, Finland over logging practices
WWF blasts Sweden, Finland over logging practices
-
How things stand in China-US trade tensions with Trump 2.0

-
 Most Asian markets rise after Wall Street's AI-fuelled rally
Most Asian markets rise after Wall Street's AI-fuelled rally
-
Fire-hit Hollywood awaits Oscar nominees, with 'Emilia Perez' in front

-
 New rider in town: Somalia's first woman equestrian turns heads
New rider in town: Somalia's first woman equestrian turns heads
-
Most Asian markets extend AI-fuelled rally

-
 Bangladesh student revolutionaries' dreams dented by joblessness
Bangladesh student revolutionaries' dreams dented by joblessness
-
Larry Ellison, tech's original maverick, makes Trump era return

-
 Political crisis hits South Korea growth: central bank
Political crisis hits South Korea growth: central bank
-
Photonis Launches Two Market-Leading Solutions to Advance Single Photon Detection and Imaging Applications
-
 Les Paul owned by guitar god Jeff Beck auctioned for over £1 mn
Les Paul owned by guitar god Jeff Beck auctioned for over £1 mn
-
Musk bashes Trump-backed AI mega project

-
 Does China control the Panama Canal, as Trump claims?
Does China control the Panama Canal, as Trump claims?
-
Yemen's Huthis say freed detained ship's crew after Gaza truce

-
 Mel B, Trump and Milei: What happened at Davos Wednesday
Mel B, Trump and Milei: What happened at Davos Wednesday
-
Argentina's Milei says would leave Mercosur for US trade deal

-
 Fashion world 'afraid' of Trump, says Van Beirendonck
Fashion world 'afraid' of Trump, says Van Beirendonck
-
P&G sees China improvement but consumers 'still struggling'

-
 Stock markets mostly higher as they track Trump plans, earnings
Stock markets mostly higher as they track Trump plans, earnings
-
Anti-Semitic acts at 'historic' highs in France despite 2024 fall: council

-
 Trump's meme coin venture sparks backlash
Trump's meme coin venture sparks backlash
-
Global green energy push likely to continue despite Trump climate retreat: UN

-
 Prince Harry settles lawsuit against Murdoch's UK tabloids
Prince Harry settles lawsuit against Murdoch's UK tabloids
-
Stock markets diverge tracking Trump plans

-
 Sudan 'political' banknote switch causes cash crunch
Sudan 'political' banknote switch causes cash crunch
-
Masa Son, Trump's Japanese buddy with the Midas Touch

-
 Borussia Dortmund sack coach Nuri Sahin after Champions League setback
Borussia Dortmund sack coach Nuri Sahin after Champions League setback
-
'Love for humanity': Low-crime Japan's unpaid parole officers

-
 Brazil saw 79% jump in area burned by fires in 2024: monitor
Brazil saw 79% jump in area burned by fires in 2024: monitor
-
No home, no insurance: The double hit from Los Angeles fires


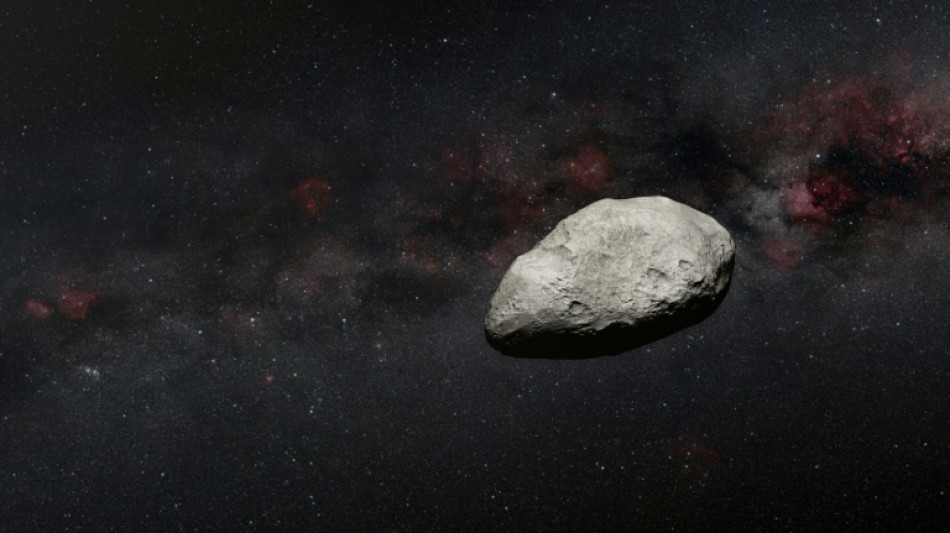
Nuking a huge asteroid could save Earth, lab experiment suggests
Humanity could use a nuclear bomb to deflect a massive, life-threatening asteroid hurtling towards Earth in the future, according to scientists who tested the theory in the labaratory by blasting X-rays at a marble-sized "mock asteroid".
The biggest real-life test of our planetary defences was carried out in 2022, when NASA's fridge-sized DART spacecraft smashed into a 160-metre (525-feet) wide asteroid, successfully knocking it well off course.
But for bigger asteroids, merely crashing spaceships into them will probably not do the trick.
When the roughly 10-kilometre wide Chicxulub asteroid struck the Yucatan peninsula around 66 million years ago, it is believed to have plunged Earth into darkness, sent kilometres-high tsunamis rippling around the globe and killed three quarters of all life -- including wiping out the dinosaurs.
We humans are hoping to avoid a similar fate.
There is no current threat looming, but scientists have been working on how to stave off any big asteroids that could come our way in the future.
A leading theory has been to be blow them up with a nuclear bomb -- a last-ditch plan famously depicted in the 1998 sci-fi action movie "Armageddon".
In the movie, Bruce Willis and a plucky team of drillers save Earth from an asteroid 1,000 kilometres wide -- roughly the size of Texas.
For a proof-of-concept study published in the journal Nature Physics this week, a team of US scientists worked on a much smaller scale, taking aim at a mock asteroid just 12 millimetres (half an inch) wide.
To test whether the theory would work, they used what was billed as the world's largest X-ray machine at Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico.
The machine is capable of generating "the brightest flash of X-rays in the world using 80 trillion watts of electricity", Sandia's Nathan Moore, the lead study author, told AFP.
Much of the energy created by a nuclear explosion is in the form of X-rays. Since there is no air in space, there would be no shockwave or fireball.
But the X-rays still pack a powerful punch.
- Turned into a 'rocket engine' -
For the lab experiment, the X-rays easily vaporised the surface of the mock asteroid.
The vaporising material then propelled the mock asteroid in the opposite direction, so that it effectively "turned into a rocket engine," Moore said.
It reached speeds of 250 kilometres an hour, "about as fast as a high-speed train," he added.
The test marked the first time that predictions about how X-rays would affect an asteroid had been confirmed, Moore said.
"It really proves this concept could work."
The scientists used modelling to scale up their experiment, estimating that X-rays from a nuclear blast could deflect an asteroid up to four kilometres wide -- if given enough advanced notice.
The biggest asteroids are the easiest to detect ahead of time, so "this approach could be quite viable" even for asteroids the size of the dinosaur-killing Chicxulub, Moore said.
The experiment was based on using a one-megaton nuclear weapon. The largest ever detonated was the 50-megaton Soviet Tsar Bomba.
If there was to be a planet-saving mission in the future, the nuclear bomb would need to be placed within a few kilometres of the asteroid -- and millions of kilometres away from Earth, Moore said.
- Asteroids come in many flavours -
Testing out the theory using a real nuke would be dangerous, hugely expensive -- and banned by international treaties.
But there is still plenty to be discovered before such a high-risk test.
The largest uncertainty right now is that asteroids can "come in many flavours", Moore said.
"We have to be prepared for every scenario."
For example, the asteroid hit by DART, Dimorphos, turned out to be a loosely held-together pile of rubble.
The European Space Agency's Hera mission is scheduled to launch next month on a mission to find out more about its composition -- and the finer details about how DART sent it packing.
Mary Burkey, a staff scientist at California's Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory that was not involved in the new study, has run computer simulations about using nukes on asteroids.
She praised the study, saying that "being able to match my calculations to real-life data increases the credibility of my results."
Her simulations have also demonstrated that such a mission "would be a very effective means to defend planet Earth", Burkey told AFP.
"However, in order for it to work, there must be enough time after a mission for the extra push of velocity to move the asteroid's trajectory off Earth."
A.Mykhailo--CPN



