
-
 Monopoly Go game maker Scopely to buy Pokemon Go team
Monopoly Go game maker Scopely to buy Pokemon Go team
-
Detained pro-Palestinian activist denied legal calls, lawyer tells US court

-
 Greenland to get new govt to lead independence process
Greenland to get new govt to lead independence process
-
Meet 'Pink', the new face of human evolution in Europe

-
 S.Africa revised budget gets booed despite smaller tax hike
S.Africa revised budget gets booed despite smaller tax hike
-
Stocks advance on US inflation slowing, Ukraine ceasefire plan

-
 Shares in Zara owner Inditex sink despite record profit
Shares in Zara owner Inditex sink despite record profit
-
US consumer inflation cools slightly as tariff worries flare

-
 Greenland to get new government to lead independence process
Greenland to get new government to lead independence process
-
Stocks diverge over Trump tariffs, Ukraine ceasefire plan

-
 Battery maker Northvolt files for bankruptcy in Sweden
Battery maker Northvolt files for bankruptcy in Sweden
-
Markets mixed as Trump trade policy sows uncertainty

-
 'Stranded' astronauts closer to coming home after next ISS launch
'Stranded' astronauts closer to coming home after next ISS launch
-
Thailand sacks senior cop over illicit gambling, fraud

-
 What to know about Manus, China's latest AI assistant
What to know about Manus, China's latest AI assistant
-
US tariffs of 25% on steel, aluminum imports take effect

-
 Trove of dinosaur footprints found at Australian school
Trove of dinosaur footprints found at Australian school
-
Rubio heads to Canada as Trump wages trade war

-
 Most Asian stocks drop as Trump trade policy sows uncertainty
Most Asian stocks drop as Trump trade policy sows uncertainty
-
Morocco fights measles outbreak amid vaccine misinformation

-
 Trump talks up Tesla in White House show of support for Musk
Trump talks up Tesla in White House show of support for Musk
-
Oil companies greet Trump return, muted on tariffs

-
 Trump burnishes Tesla at White House in show of support for Musk
Trump burnishes Tesla at White House in show of support for Musk
-
Italian defence firm Leonardo to focus on int'l alliances for growth

-
 Stock markets extend losses over US tariffs, recession fears
Stock markets extend losses over US tariffs, recession fears
-
Trump doubles down on Canada trade war with major tariff hike

-
 UK makes manslaughter arrest over North Sea ship crash
UK makes manslaughter arrest over North Sea ship crash
-
Ghana scraps IMF-linked 'nuisance' taxes

-
 Trump doubles down on Canada trade war with massive new tariffs
Trump doubles down on Canada trade war with massive new tariffs
-
French right-wing media's Russia tilt irks Elysee

-
 Stock markets waver after sell-off over US recession fears
Stock markets waver after sell-off over US recession fears
-
Volkswagen to navigate another tricky year after 2024 profit plunge

-
 Ships blaze after North Sea crash, govt rules out foul play
Ships blaze after North Sea crash, govt rules out foul play
-
Chanel plays with proportions as Paris Fashion Week wraps up

-
 Stock markets mixed as Trump-fuelled economy fears weigh
Stock markets mixed as Trump-fuelled economy fears weigh
-
Ships blaze, spill feared after North Sea crash

-
 Volkswagen profits hit as high costs, China woes weigh
Volkswagen profits hit as high costs, China woes weigh
-
Struggling Japanese automaker Nissan replaces CEO

-
 Ships still on fire after North Sea crash
Ships still on fire after North Sea crash
-
Lego posts record profit, CEO shrugs off US tariff threat

-
 Most markets in retreat as Trump-fuelled economy fears build
Most markets in retreat as Trump-fuelled economy fears build
-
Asian markets track Wall St lower as Trump-fuelled economy fears build

-
 From 'mob wives' to millennials: Faux fur is now a fashion staple
From 'mob wives' to millennials: Faux fur is now a fashion staple
-
South Korea's Kia denies responsibility for anti-Musk ad

-
 Kung fu girl group puts fresh spin on ancient Chinese art
Kung fu girl group puts fresh spin on ancient Chinese art
-
Asian markets track Wall St selloff as Trump-fuelled economy fears build

-
 Indian artisans keep traditional toymaking alive
Indian artisans keep traditional toymaking alive
-
Bear Robotics' Carti 100 Wins iF DESIGN AWARD 2025, Setting New Standards in Logistics Automation

-
 Formerra Introduces Formerra+ Upgraded Ecommerce Site to Optimize Customer Experience
Formerra Introduces Formerra+ Upgraded Ecommerce Site to Optimize Customer Experience
-
Search ends for missing crew member after North Sea collision


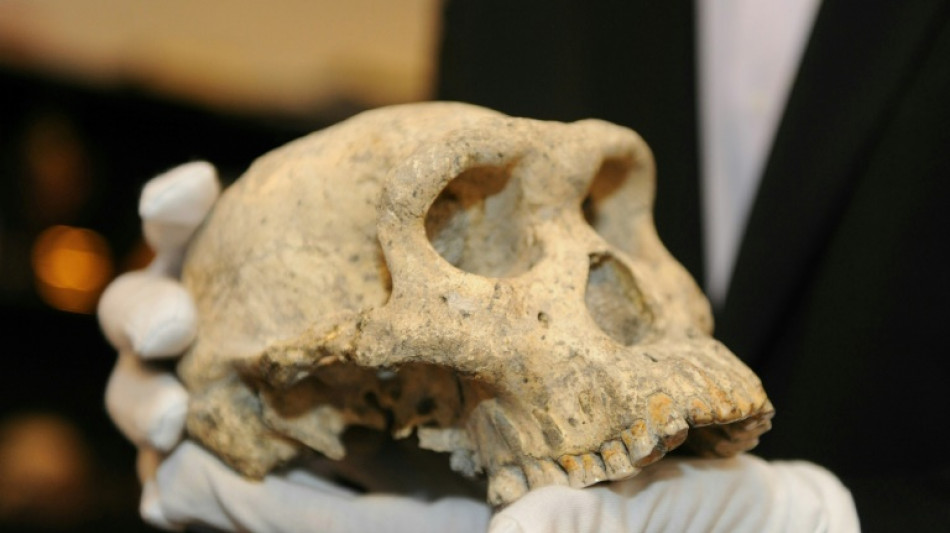
Meet 'Pink', the new face of human evolution in Europe
Western Europe has a new oldest face: the facial bones of an adult nicknamed "Pink" discovered in Spain are from a potential new member of the human family who lived more than 1.1 million years ago, scientists said Wednesday.
Until now, the oldest-known human species in Western Europe was the slender-faced Homo antecessor, dating back around 850,000 years.
But research published in the journal Nature "introduces a new actor in the history of human evolution in Europe", lead study author Rosa Huguet of Spain's University of Rovira i Virgili told a press conference.
The fossilised upper jawbone and partial cheekbone of Pink were discovered at the Atapuerca archaeological site in northern Spain in 2022.
Since then, a team of Spanish scientists have been working to find out more about Pink, whose nickname is a reference to prog rock band Pink Floyd.
The bones were excavated from a layer of silt and red mud 16 metres (52 feet) deep at a site known as Sima del Elefante -- or "elephant pit".
They were found less than 250 metres from where the fossils of Western Europe's previous oldest human, Homo antecessor, were discovered nearly two decades ago.
But the title of oldest human in all of Europe is still held by the Dmanisi people -- also called Homo georgicus -- who lived up to 1.8 million years ago in what is now Georgia.
They were the first members of the human family, or hominins, known to have made it to Europe from Africa, the cradle of humanity.
We modern Homo sapiens first showed up in Africa around 300,000 years ago -- and took our time getting to Europe.
- Face value -
The Spanish researchers used 3D imaging techniques to flesh out Pink's full face.
Homo antecessor had a "very modern" face which is "vertical and flat" similar to our own, said Maria Martinon-Torres, director of Spain's National Research Center on Human Evolution.
But Pink's face is more "projected forward and more robust," the study co-author added.
This means it bears some similarities to the face of Homo erectus -- but not enough that the scientists could confirm that Pink was a member of this important human ancestor.
So the scientists made up a new name for the possible species that Pink could belong to: Homo "affinis" erectus.
"This is the most honest proposal we can make with the evidence we have," Martinon-Torres said.
From just a few face bones, the researchers could not determine Pink's age or gender.
But by analysing small stone tools and animals bones found at the site, they were able to get an idea of the environment Pink lived in.
It was a humid forest landscape, roamed by horses, ancient cattle, monkeys and even some hippos.
The area was a wildlife corridor with plenty of water, making it an "ideal" place for our ancient relatives to settle, Huguet said.
- What happened to them? -
The new discovery supports the hypothesis that early humans settled Europe going from east to west at least 1.4 million years ago, according to the Spanish researchers.
If Pink is a representative of a previously unknown human species, it could have been a bridge between the Dmanisi hominins and Homo antecessors, they added.
But this raises another question: what became of these people?
Spanish paleoanthropologist Jose Maria Bermudez de Castro felt that Pink's people likely did not survive a severe human "bottleneck" nearly 900,000 years ago thought to have been caused by global cooling.
"I think that Homo affinis erectus probably disappeared," the study co-author said.
Future research will aim to shed light on these mysteries. The Spanish team has not yet reached the bottom of the elephant pit -- nor other sites around it.
H.Meyer--CPN
