
-
 From oil spills to new species: how tech reveals the ocean
From oil spills to new species: how tech reveals the ocean
-
Former sex worker records Tokyo's red-light history

-
 Most Asian markets rise on hopes for bill to avert US shutdown
Most Asian markets rise on hopes for bill to avert US shutdown
-
Renowned US health research hub Johns Hopkins to slash 2,000 jobs

-
 You're kidding! Prince William reveals Aston Villa superstitions
You're kidding! Prince William reveals Aston Villa superstitions
-
Top US university says ending 2,000 positions due to Trump cuts

-
 Stock markets tumble as Trump targets booze
Stock markets tumble as Trump targets booze
-
Sea levels rise by 'unexpected' amount in 2024: NASA

-
 Trump tariff threat leaves sour taste for European drinks producers
Trump tariff threat leaves sour taste for European drinks producers
-
Ex-NOAA chief: Trump firings put lives, jobs, and science in jeopardy

-
 Spain to face increasingly 'severe' droughts: report
Spain to face increasingly 'severe' droughts: report
-
Georgian designer Demna leaves Balenciaga for Gucci

-
 Diet puts Greenland Inuit at risk from 'forever chemicals': study
Diet puts Greenland Inuit at risk from 'forever chemicals': study
-
'Blood Moon' rising: Rare total lunar eclipse tonight

-
 Donatella Versace, fashion icon who saved slain brother's brand
Donatella Versace, fashion icon who saved slain brother's brand
-
Sweden to hold talks on countering soaring food costs

-
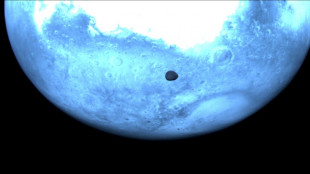 Asteroid probe snaps rare pics of Martian moon
Asteroid probe snaps rare pics of Martian moon
-
EU, US eye greater energy ties amid Trump frictions

-
 Donatella Versace to give up creative reins of brand after 28 years
Donatella Versace to give up creative reins of brand after 28 years
-
Stock markets find little cheer as Trump targets champagne

-
 UK seeks tougher term for father jailed over daughter's murder
UK seeks tougher term for father jailed over daughter's murder
-
Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan sign border deal to boost regional stability

-
 First brown bear to have brain surgery emerges from hibernation
First brown bear to have brain surgery emerges from hibernation
-
Iraq says seeking alternatives to Iran gas

-
 Food app Deliveroo delivers first annual profit
Food app Deliveroo delivers first annual profit
-
Less mapped than the Moon: quest to reveal the seabed

-
 Couche-Tard bosses make case in Tokyo for 7-Eleven buyout
Couche-Tard bosses make case in Tokyo for 7-Eleven buyout
-
Australia tells US influencer: 'leave baby wombat alone'

-
 'Sound science' must guide deep-sea mining: top official
'Sound science' must guide deep-sea mining: top official
-
Asian stocks wobble as US inflation fails to ease trade worries

-
 Trump's Canada fixation: an expansionist dream
Trump's Canada fixation: an expansionist dream
-
Generative AI rivals racing to the future

-
 DeepSeek dims shine of AI stars
DeepSeek dims shine of AI stars
-
Americas to witness rare 'Blood Moon' total lunar eclipse
-
 More wait for stranded astronauts after replacement crew delayed
More wait for stranded astronauts after replacement crew delayed
-
Argentine football fans, protesters clash with police at pensions march

-
 Monopoly Go game maker Scopely to buy Pokemon Go team
Monopoly Go game maker Scopely to buy Pokemon Go team
-
Detained pro-Palestinian activist denied legal calls, lawyer tells US court

-
 Greenland to get new govt to lead independence process
Greenland to get new govt to lead independence process
-
Meet 'Pink', the new face of human evolution in Europe

-
 S.Africa revised budget gets booed despite smaller tax hike
S.Africa revised budget gets booed despite smaller tax hike
-
Stocks advance on US inflation slowing, Ukraine ceasefire plan

-
 Shares in Zara owner Inditex sink despite record profit
Shares in Zara owner Inditex sink despite record profit
-
US consumer inflation cools slightly as tariff worries flare

-
 Greenland to get new government to lead independence process
Greenland to get new government to lead independence process
-
Stocks diverge over Trump tariffs, Ukraine ceasefire plan

-
 Battery maker Northvolt files for bankruptcy in Sweden
Battery maker Northvolt files for bankruptcy in Sweden
-
Markets mixed as Trump trade policy sows uncertainty

-
 'Stranded' astronauts closer to coming home after next ISS launch
'Stranded' astronauts closer to coming home after next ISS launch
-
Thailand sacks senior cop over illicit gambling, fraud


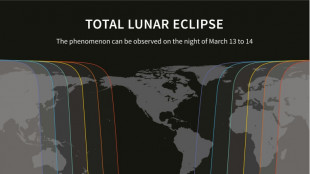
Americas to witness rare 'Blood Moon' total lunar eclipse
Stargazers in North and South America will be able to view a red-colored "Blood Moon" starting Thursday night in the first total lunar eclipse visible on the continents since 2022.
The celestial event, observable with the naked eye, will have more than an hour of totality and can additionally be seen in parts of western Europe and Africa, as well as New Zealand.
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth goes between the Moon and the Sun, casting the Earth's shadow on the Moon.
A rare total lunar eclipse involves the Earth's umbra, the darkest part of the planet's shadow, covering the Moon.
According to NASA, this type of eclipse can also be called a "Blood Moon" due to the reddish-orange color the Moon can become during totality.
The coloration occurs due to sunlight scattering through the Earth's atmosphere before reaching the Moon's surface -- shorter wavelengths like blue and violet fail to reach the Moon, leaving only longer wavelengths such as red and orange to illuminate it.
As a result, the more items there are in the Earth's atmosphere -- such as clouds or dust -- the redder the Moon will appear during the eclipse.
"Keep a close eye on the weather forecast leading up to the eclipse," said NASA Chief Scientist Renee Weber in a statement. "That totality will last for close to an hour, so even if it's cloudy you may still be able to glimpse it if the clouds are scattered."
The timing of totality occurs simultaneously across time zones, and is expected to begin at 2:26 am Friday for those in Eastern Daylight Time and 11:26 pm Thursday in Pacific Daylight Time.
For about an hour both before and after totality, the moon will also be obscured in a partial eclipse.
P.Schmidt--CPN
