-
 Gabon early results show voters back new constitution
Gabon early results show voters back new constitution
-
Is AI's meteoric rise beginning to slow?

-
 Biden touts climate legacy in landmark Amazon visit
Biden touts climate legacy in landmark Amazon visit
-
Biden clears Ukraine for long-range missile strikes inside Russia

-
 'Nobody can reverse' US progress on clean energy: Biden
'Nobody can reverse' US progress on clean energy: Biden
-
Biden allows Ukraine to strike Russia with long-range missiles: US official

-
 Biden clears Ukraine for missile strikes inside Russia
Biden clears Ukraine for missile strikes inside Russia
-
Ukrainians brave arduous journeys to Russian-occupied homeland

-
 'Devil is in the details,' EU chief says of S.America trade deal
'Devil is in the details,' EU chief says of S.America trade deal
-
Toll in Tanzania building collapse rises to 13, survivors trapped

-
 'Red One' tops N.America box office but could end up in the red
'Red One' tops N.America box office but could end up in the red
-
Biden begins historic Amazon trip amid Trump climate fears

-
 Macron defends French farmers in talks with Argentina's Milei
Macron defends French farmers in talks with Argentina's Milei
-
India and Nigeria renew ties as Modi visits

-
 Typhoon Man-yi weakens as it crosses Philippines' main island
Typhoon Man-yi weakens as it crosses Philippines' main island
-
迪拜棕榈岛索菲特美憬阁酒店: 五星級健康綠洲

-
 The Retreat Palm Dubai MGallery by Sofitel: Пятизвездочный велнес-оазис
The Retreat Palm Dubai MGallery by Sofitel: Пятизвездочный велнес-оазис
-
The Retreat Palm Dubai MGallery by Sofitel: A five-star wellness Oasis

-
 Power cuts as Russian missiles pound Ukraine's energy grid
Power cuts as Russian missiles pound Ukraine's energy grid
-
Biden in historic Amazon trip as Trump return sparks climate fears

-
 India hails 'historic' hypersonic missile test flight
India hails 'historic' hypersonic missile test flight
-
Debt-saddled Laos struggles to tame rampant inflation

-
 India's vinyl revival finds its groove
India's vinyl revival finds its groove
-
Climate finance can be hard sell, says aide to banks and PMs

-
 Egypt's middle class cuts costs as IMF-backed reforms take hold
Egypt's middle class cuts costs as IMF-backed reforms take hold
-
Dinosaur skeleton fetches 6 million euros in Paris sale

-
 Trump's Republican allies tread lightly on Paris pact at COP29
Trump's Republican allies tread lightly on Paris pact at COP29
-
China's Xi urges APEC unity in face of 'protectionism'

-
 Farmers target PM Starmer in protest against new UK tax rules
Farmers target PM Starmer in protest against new UK tax rules
-
UN climate chief urges G20 to spur tense COP29 negotiations

-
 Philippines warns of 'potentially catastrophic' Super Typhoon Man-yi
Philippines warns of 'potentially catastrophic' Super Typhoon Man-yi
-
Tens of thousands flee as Super Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines

-
 Gabon votes on new constitution hailed by junta as 'turning point'
Gabon votes on new constitution hailed by junta as 'turning point'
-
Tens of thousands flee as Typhoon Man-yi nears Philippines

-
 Is Argentina's Milei on brink of leaving Paris climate accord?
Is Argentina's Milei on brink of leaving Paris climate accord?
-
Fitch upgrades Argentina debt rating amid economic pain

-
 Trump picks Doug Burgum as energy czar in new administration
Trump picks Doug Burgum as energy czar in new administration
-
At summit under Trump shadow, Xi and Biden signal turbulence ahead

-
 Xi warns against 'protectionism' at APEC summit under Trump cloud
Xi warns against 'protectionism' at APEC summit under Trump cloud
-
Xi, Biden at Asia-Pacific summit under Trump trade war cloud

-
 Leftist voices seek to be heard at Rio's G20 summit
Leftist voices seek to be heard at Rio's G20 summit
-
Boeing strike will hurt Ethiopian Airlines growth: CEO

-
 US retail sales lose steam in October after hurricanes
US retail sales lose steam in October after hurricanes
-
Spate of child poisoning deaths sparks S.Africa xenophobia

-
 Comedian Conan O'Brien to host Oscars
Comedian Conan O'Brien to host Oscars
-
Gore says 'absurd' to hold UN climate talks in petrostates

-
 Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts
Global stocks struggle after Fed signals slower rate cuts
-
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks

-
 Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence
-
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump


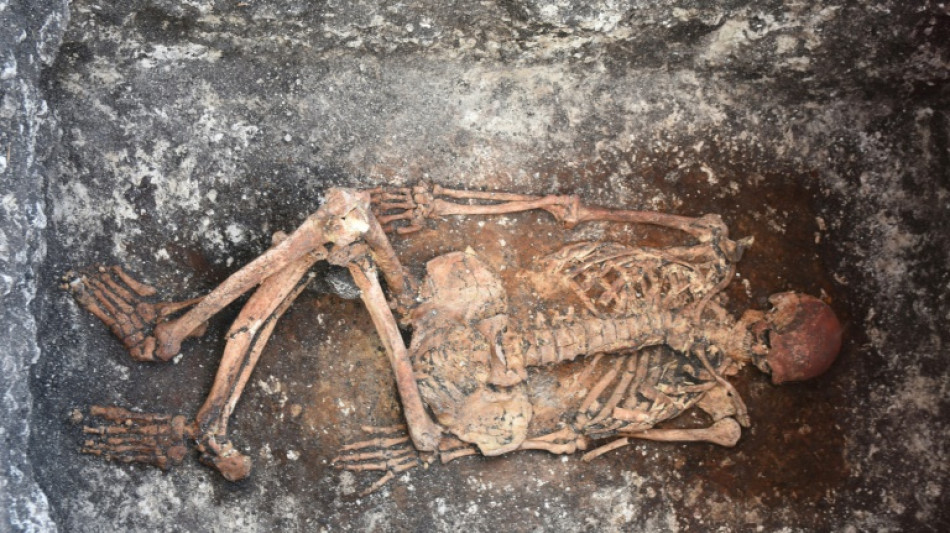
Horseback riding may have begun 5,000 years ago in Europe: study
Who were the first people to ride horses?
Researchers believe they have found the earliest evidence of horseback riding, by the ancient Yamnaya people in Europe some 5,000 years ago.
Their conclusions, based on an analysis of human skeletal remains found in Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania, were published on Friday in the journal Science Advances.
Domestication of horses for milk is widely accepted to have begun around 3500 BC to 3000 BC, the study said, but the "origins of horseback riding remain elusive."
The researchers from the University of Helsinki and other European institutions date the earliest horsemanship to 3000 BC to 2500 BC among members of the Yamnaya culture.
"Our findings provide a strong argument that horseback riding was already a common activity for some Yamnaya individuals as early as 3000 BC," the researchers said.
Horse bones have been discovered in Yamnaya settlements but they are not as well preserved as human skeletons, which were given proper burials in earth-covered mounds known as "kurgans."
The researchers said the human skeletons provided the best source of information about horse riding because any riding tack used by early riders would have been made using perishable materials.
The researchers said some of the human skeletons they analyzed bore skeletal traits indicative of what they called "horsemanship syndrome."
"A skeleton of a living person is reacting," Martin Trautmann, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Helsinki and one of the authors of the study, told AFP.
"If you sit on horseback you need to balance with every step of your mount, you need to cling tightly with your legs."
Doing that repeatedly leaves tell-tale changes in bone morphology, Trautmann said, including "stress-induced vertebral degeneration," a common ailment among avid horse riders.
"We know that saddles and stirrups dated much later," Trautmann said, and the early horse riders were probably riding bareback and gripping the mane of the horse.
- 'Cowboys, not warriors' -
Volker Heyd, a professor of archeology at the University of Helsinki, said the findings "fit very nicely into the overall picture" of Yamnaya culture.
"We were already suspecting them of using horses," Heyd said, and it could help explain the "exceptional" geographic expansion of their society in a few generations.
"It is difficult to envision how this expansion could have taken place without improved means of transport," the researchers said.
"Using horses for transport was a decisive step in human cultural development," they said.
"Trade and cultural exchange as well as conflicts and migrations leapt with the increase in speed and range provided by horsemanship."
The researchers said the Yamnaya were probably not initially using horses for warfare.
"They were cowboys, not warriors," said Trautmann.
Heyd said the early horse riders "were probably helping the Yamnaya people in guarding their animals, their cattle and sheep mostly."
According to the researchers, the earliest figurative evidence of horse riding comes from the Mesopotamian Ur III period shortly before 2000 BC through depictions of a horse and rider.
Images and mentions in cuneiform texts of horseback riding are also found in the Old Babylonian period from around 1880 BC to 1595 BC.
X.Wong--CPN


